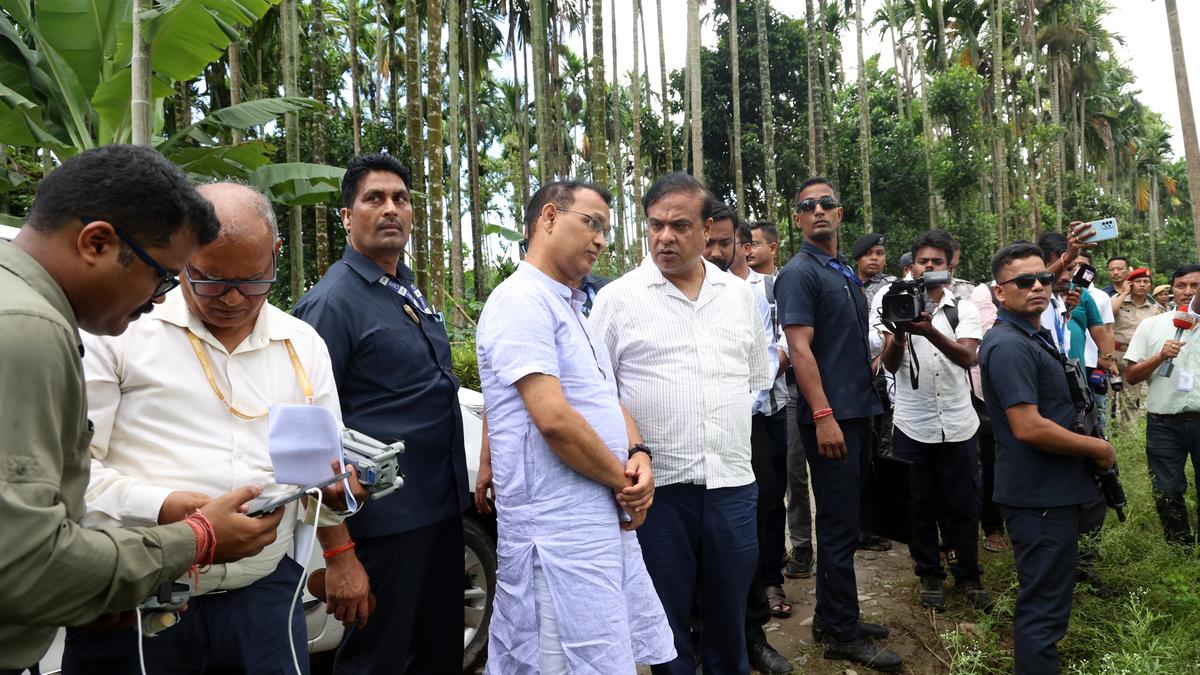
Assam Chief Minister Himanta Biswa Sarma with others during an inspection of sites for eviction drives at Uriamghat, in Golaghat district, Assam, on July 25, 2025
| Photo Credit: CMO Assam
The story so far: The Assam government’s drive to evict encroachers from forestlands has sent alarm bells ringing in other States of the region. Now, States bordering Assam are taking measures to ensure that those evicted from Assam do not cross over.
When did the eviction drive start in Assam?
The BJP came to power in 2016 by promising to secure jaati (race), maati (land), and bheti (hearth). Based on a Gauhati High Court order to reclaim encroached forestlands, the first eviction drive was carried out in three fringe villages of eastern Assam’s Kaziranga National Park in September 2016. Two people died at Gorukhuti in north-central Assam’s Darrang district when the eviction drive resumed in September 2021, five months after the BJP retained power and Himanta Biswa Sarma became Chief Minister. The eviction drives, allegedly targeted at Bengali Muslims, resumed in June 2025, coinciding with charges of corruption against the BJP-led government, one of them involving the purchase and redistribution of Gir cows for an agricultural project at Gorukhuti, from where migrant Muslims were evicted.

What are the roots of the problem?
Evicting encroachers from forestlands, wetlands, and government revenue lands is not a new phenomenon in Assam. However, the operation has been high on optics as the BJP and its sub-nationalist regional allies have accused the 15-year rule by Congress of having paved the ground for encroachment by the ‘Bangladeshi’, ‘Miya’, or ‘illegal infiltrators’ — pejoratives for Muslims with roots in present-day Bangladesh — for votes. This category of Muslims has long polarised electoral politics in Assam during and after the anti-foreigners Assam Agitation (1979-’85), which led to the signing of an accord prescribing a cut-off date — midnight of March 24, 1971 — for the detection, deletion (from electoral rolls), and deportation of “illegal immigrants” or Bangladeshi nationals.
Why is the drive overtly aggressive?
The eviction drives have impacted non-Muslims as well, including 130 families whose houses were bulldozed to clear the Silsako Beel, a major wetland in Guwahati, of encroachment in 2022. Those against migrant Muslims, however, has garnered more attention for their scale and intensity, as it has led to the death of at least five people between 2016 and July 2025, when 1,080 families were evicted from 135 hectares of the Paikan Reserve Forest in Assam’s Goalpara district. This aggression is also reflected in the rhetoric of the Chief Minister and other BJP leaders, who refer to the drive as a long-term exercise to save Assam from ‘land jihad’.

Before the drive was launched this year, the Chief Minister said 15,288.52 bighas of satra (Vaishnav monastery) lands remain illegally occupied by people of doubtful citizenship across 29 districts. He also referred to the Union Environment Ministry’s report to the National Green Tribunal that 3,620.9 square kilometres of forest area in Assam were under encroachment as of March 2024. The Chief Minister vowed to continue the eviction drive until Assam is encroachment-free in “at least 10 years”, while clarifying that tribal people living in forest areas from before 2005 and covered by the Forest Rights Act would not be touched. This followed the fast-track resettlement of at least 12 Ahom families who were evicted along with migrant Muslims from village grazing reserves across four locations in northeastern Assam’s Lakhimpur district.
Why are Assam’s neighbours jittery?
Assam’s neighbours were passive as long as the eviction drives were in areas far from the interstate borders. NGOs in Nagaland stirred into action after the Assam government announced an anti-encroachment drive in Golaghat district’s Uriamghat. They saw it as a move to push “illegal Bangladeshi immigrants” inside Nagaland under the agenda of usurping “ancestral Naga lands”. Before the drive commenced, the police in Nagaland’s Niuland district intercepted and turned 200 vehicles carrying “illegal migrants” back to Assam. A few days later, a conglomerate of extremist groups announced a task force to guard the Assam-Nagaland border against infiltrators. The governments of Manipur, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, and Mizoram followed suit. They issued orders to the authorities in areas bordering Assam to increase vigilance, prevent the evicted people from coming in, and make the issuance of the inner-line permit, a temporary travel document, stricter.
How are border disputes linked to eviction?
Although opposition political parties in Assam see the eviction drive against Bengali-speaking Muslims as a part of the BJP’s agenda of polarisation ahead of the 2026 Assembly polls, encroachment is at the core of the State’s boundary disputes with Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Nagaland. These States were carved out of Assam between 1963 and 1972. In March 2025, the Assam Assembly was told that the four States have been occupying almost 83,000 hectares of land belonging to the State. These States have, off and on, driven migrant Muslims out to Assam, a State they accuse of having patronised “illegal immigrants” and made them settle along the borders as a ploy to claim disputed lands. More than 350 people have died due to the inter-State disputes, which Assam has partially resolved with Arunachal Pradesh and Meghalaya. On July 30, the Gauhati High Court directed these five States to constitute a high-level committee to facilitate a coordinated action to clear illegal settlements from forestlands.
Published – August 03, 2025 03:09 am IST